What is disaster recovery planning?
Disaster recovery planning is a proactive and strategic approach that organisations undertake to prepare for and mitigate the impact of unforeseen events that can disrupt their operations. It involves creating a comprehensive roadmap and set of procedures to restore critical systems and processes after a disaster, enabling businesses to resume normal operations as quickly and smoothly as possible. The goal is to minimise downtime, protect data integrity, and ensure business continuity in the face of various disasters, such as natural calamities, cyberattacks, hardware failures, or human errors.
IT disaster recovery planning vs ICT disaster recovery planning
IT disaster recovery planning and ICT (Information and Communication Technology) disaster recovery planning are often used interchangeably, but they have subtle differences. IT DR planning focuses primarily on the recovery of technology systems, such as servers, networks, databases, and applications. It entails identifying critical IT assets, creating backup and restoration mechanisms, and establishing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each system.
On the other hand, ICT disaster recovery planning encompasses a broader scope by including not only IT systems but also other communication and information technologies. This includes telecommunication networks, internet connectivity, collaboration tools, and other ICT infrastructure that organisations rely on for their day-to-day operations. ICT disaster recovery planning ensures the availability and continuity of all essential technologies required to support business processes during and after a disaster.
Business disaster recovery planning Steps

Business disaster recovery planning is an overarching strategy that encompasses the entire organisation’s operations, beyond just IT or ICT systems. It involves a holistic approach to identify critical business functions, assess potential risks and vulnerabilities, and develop comprehensive recovery strategies. The aim is to restore not only technology infrastructure but also key business processes, personnel, facilities, and other vital resources.
In business disaster recovery planning, organisations typically conduct a s (BIA) to evaluate the potential financial, operational, and reputational impacts of various disasters. This analysis helps prioritise recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively. Business continuity plans are then developed, outlining specific actions, roles and responsibilities, and the necessary steps to resume operations swiftly and minimise disruptions.
Disaster recovery planning in cloud computing
Disaster recovery planning in cloud computing leverages the advantages of cloud infrastructure and services to enhance resilience and recovery capabilities. With traditional disaster recovery approaches, organisations often face challenges such as expensive hardware investments, complex setup processes, and limited scalability. Cloud-based disaster recovery eliminates many of these hurdles.
By leveraging cloud computing, organisations can replicate and back up their critical data and systems in multiple geographically diverse locations. This redundancy ensures that if one data centre or server becomes unavailable, the workload can seamlessly shift to another location, minimising downtime. Cloud disaster recovery also offers the flexibility to scale resources up or down as needed, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
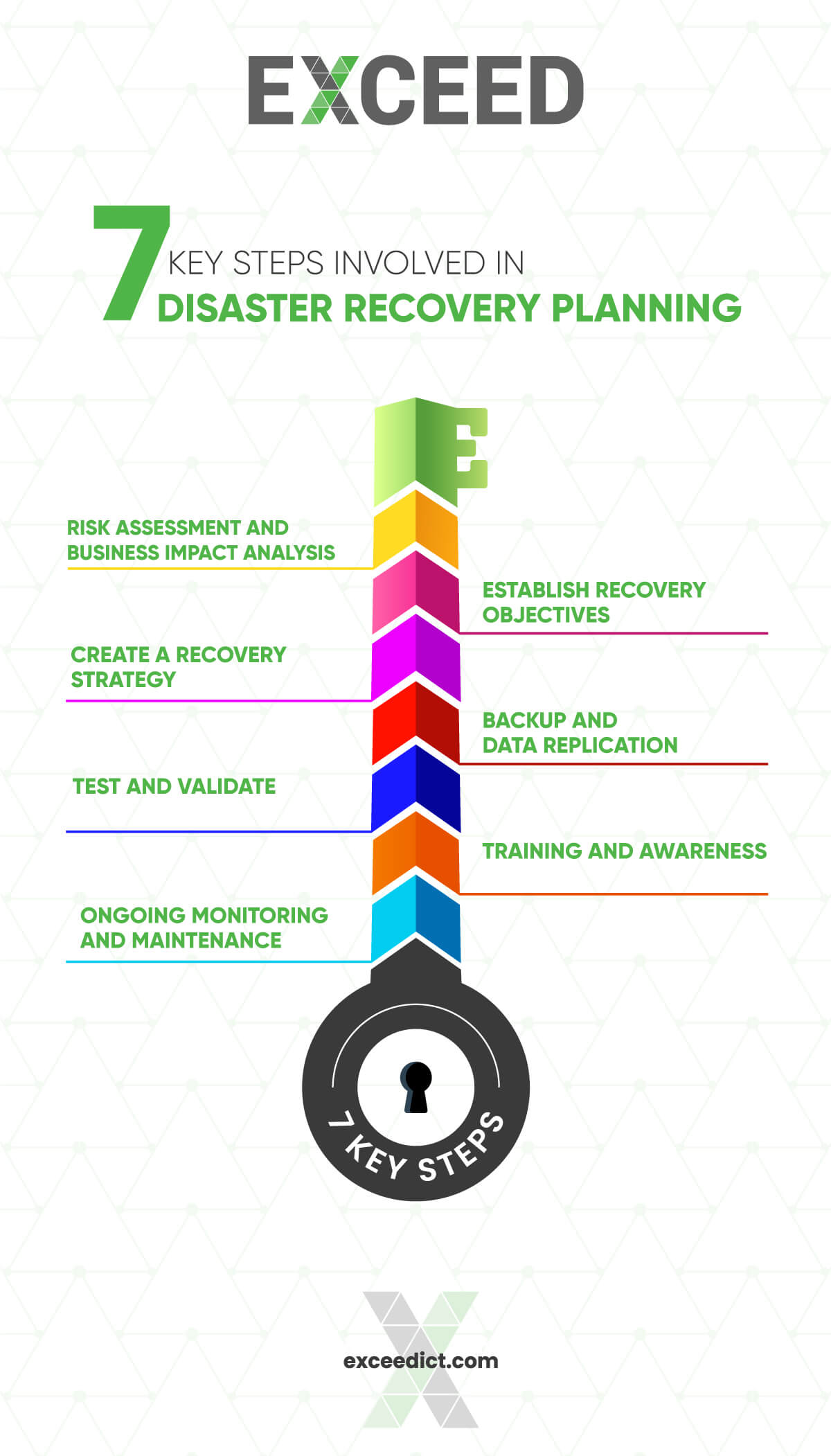
Disaster recovery planning steps
 While the specific steps in a disaster recovery plan may vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and unique requirements, there are some common elements to consider.
While the specific steps in a disaster recovery plan may vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and unique requirements, there are some common elements to consider.
Here are the key steps involved in Disaster recovery planning steps:
Step 1: Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis: Identify potential risks, assess their likelihood and potential impact on critical business functions.
Step 2: Establish Recovery Objectives: Define recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for different systems and processes.
Step 3: Create a Recovery Strategy: Develop a comprehensive plan detailing the steps, procedures, and resources required for recovery in different disaster scenarios.
Step 4: Backup and Data Replication: Implement robust backup mechanisms and data replication strategies to ensure data integrity and availability.
Step 5: Test and Validate: Regularly test the disaster recovery plan to identify gaps or weaknesses, refine procedures, and validate the effectiveness of recovery strategies.
Step 6: Training and Awareness: Train employees on their roles and responsibilities during a disaster and raise awareness about the importance of disaster recovery planning.
Step 7: Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the plan, update it as needed, and keep up with technological advancements and evolving threats.
Benefits of DR planning
Implementing a robust disaster recovery plan offers several significant benefits to organisations:
- Minimised Downtime: Quick recovery and restoration of critical systems reduce downtime, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations.
- Data Protection and Integrity: Backups and replication mechanisms safeguard data integrity, preventing data loss and enabling swift recovery.
- Regulatory Compliance: A well-designed disaster recovery plan helps organisations meet industry-specific regulatory requirements and data protection laws.
- Business Continuity: By having a tested and reliable recovery strategy, organisations can maintain continuity during and after a disaster, protecting revenue and customer trust.
- Cost Savings: Effective disaster recovery planning can mitigate financial losses associated with downtime, reputational damage, and potential legal liabilities.
Disaster recovery planning best practices
To ensure the effectiveness of a disaster recovery plan, organisations should follow these best practices:
a) Regularly review and update the plan to incorporate changes in technology, processes, and potential risks.
b) Conduct thorough testing and validation exercises to identify gaps or weaknesses and refine recovery procedures.
c) Maintain clear documentation of procedures, roles, and responsibilities to ensure smooth execution during a crisis.
d) Establish communication channels and protocols to keep stakeholders informed during a disaster and provide timely updates on recovery progress.
e) Train employees on their specific roles and responsibilities in executing the disaster recovery plan.
f) Regularly assess and prioritise critical systems, applications, and data to ensure appropriate levels of protection and recovery.
g) Periodically audit and evaluate third-party vendors’ disaster recovery capabilities if they are involved in critical business operations.
By adopting these best practices, organisations can enhance their resilience, minimise the impact of disasters, and ensure the continuity of their business operations in even the most challenging
Call us on 1300 832 639 or simply search “Exceed ICT” on Google Maps to find a location near you and connect with our team today.
We also provide
Telecoms Expense Management, Device Deployment, Fleet management, Telstra enterprise Mobility, Telstra mobility Managed Services.
Improve Business Core values, Business Consulting, Network Management, Telstra Expense Management and many more Services.