
Disaster recovery planning is crucial for every business, regardless of size or industry. When a disaster strikes, whether it’s a natural calamity, cyber-attack, or equipment failure, having a well-prepared and thoroughly tested recovery plan can mean the difference between swift recovery and significant downtime. In this article, we will explore the essential components that should be included in a disaster recovery testing plan to help businesses ensure business continuity and data integrity.
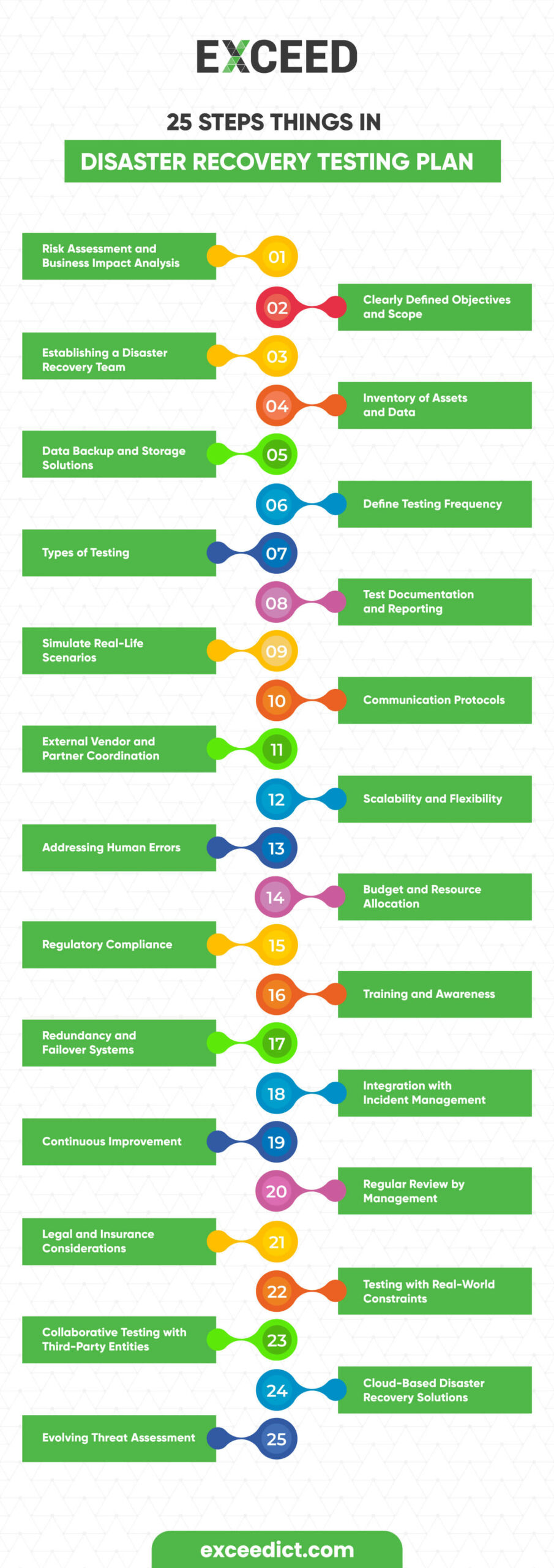
What to Include in a Disaster Recovery Testing Plan?
A disaster recovery testing plan must encompass various elements to ensure its effectiveness and reliability. Below, we’ve outlined the key components that should be included.
 Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
Before crafting a disaster recovery testing plan, conduct a comprehensive risk assessment and business impact analysis. Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to your organisation, and evaluate the potential impact of disruptions on critical business processes. This information will guide your disaster recovery strategy.
Clearly Defined Objectives and Scope
Outline the specific objectives and scope of your disaster recovery testing plan. Define what you aim to achieve through testing, such as verifying recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), and identifying areas for improvement.
Establishing a Disaster Recovery Team
Form a dedicated disaster recovery team consisting of individuals from different departments with expertise in IT, operations, and management. Designate clear roles and responsibilities to ensure seamless execution during testing and actual disaster situations.
Inventory of Assets and Data
Create an inventory of all critical assets, including hardware, software, applications, and data. Prioritise assets based on their importance to business operations, and ensure all essential data is included in the recovery plan.
Data Backup and Storage Solutions
Implement robust data backup and storage solutions to ensure redundant copies of critical data are readily available. Consider both on-site and off-site backup options to protect against physical damage.
Define Testing Frequency
Determine how frequently you will conduct disaster recovery testing. Regular testing is essential to identify potential weaknesses and maintain the effectiveness of your plan.
Types of Testing
Plan and conduct various types of disaster recovery testing, such as:
- Tabletop Exercises: Simulate disaster scenarios and evaluate team response without actual execution.
- Functional Testing: Validate the functionality of individual components of the recovery plan.
- Full-Scale Testing: Execute a complete disaster recovery test to assess the overall plan’s effectiveness.
Test Documentation and Reporting
Develop detailed documentation of each test, including pre-test preparations, the testing process, and post-test evaluations. Record all findings and improvements to enhance future testing processes.
Simulate Real-Life Scenarios
Design test scenarios that closely resemble real-life disasters. This ensures that your team is well-prepared to handle the actual situation should it occur.
Communication Protocols
Establish clear communication protocols to ensure effective coordination among team members during testing and actual disaster recovery efforts.
External Vendor and Partner Coordination
If your business relies on external vendors or partners for critical services, ensure they are aware of your disaster recovery testing plan and their role in the event of a disaster.
Scalability and Flexibility
Ensure your disaster recovery plan is scalable and flexible enough to accommodate the changing needs of your organisation as it grows.
Addressing Human Errors
Recognise that human errors can be a significant factor in disaster situations. Implement measures to minimise the risk of errors during testing and actual recovery efforts.
Budget and Resource Allocation
Allocate sufficient budget and resources to support the implementation and testing of your disaster recovery plan.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that your disaster recovery testing plan complies with relevant industry regulations and data protection laws.
Training and Awareness
Regularly train employees on the disaster recovery plan and create awareness of the importance of disaster preparedness.
Redundancy and Failover Systems
Implement redundant systems and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous operations during a disaster.
Integration with Incident Management
Integrate the disaster recovery plan with your organisation’s incident management procedures to streamline response efforts.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly review and update your disaster recovery testing plan to address new threats and technologies.
Regular Review by Management
Ensure top-level management regularly reviews and approves the disaster recovery plan.
Legal and Insurance Considerations
Consult with legal experts and insurance providers to ensure your plan adequately covers all potential liabilities and risks.
Testing with Real-World Constraints
Conduct disaster recovery testing with real-world constraints, such as limited resources or time, to assess the plan’s effectiveness under challenging circumstances.
Collaborative Testing with Third-Party Entities

Collaborate with third-party entities, such as cybersecurity experts, to gain valuable insights and feedback on your disaster recovery testing plan.
Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery Solutions
Explore cloud-based disaster recovery solutions as they offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and remote accessibility.
Evolving Threat Assessment
Stay vigilant and regularly assess new threats and vulnerabilities to update your disaster recovery plan accordingly.
FAQs
Is disaster recovery testing necessary for small businesses?
Absolutely! Disaster recovery testing is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses often lack the resources to recover from a significant disaster without proper planning. Regular testing ensures preparedness and can prevent substantial financial losses.
How often should disaster recovery testing be conducted?
The frequency of disaster recovery testing depends on factors like the nature of the business, industry regulations, and the rate of infrastructure changes. In general, it is recommended to conduct tests at least annually, with additional testing for critical systems and whenever major changes occur.
What are the consequences of not having a disaster recovery testing plan?
Without a disaster recovery testing plan, businesses risk extended downtime, data loss, financial losses, damaged reputation, and potential legal consequences. The lack of preparedness could be catastrophic in the event of a disaster.
Can disaster recovery testing identify weaknesses in the plan?
Yes, disaster recovery testing is designed to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement in the recovery plan. Regular testing helps businesses address vulnerabilities and enhance their overall preparedness.
Is cloud-based disaster recovery better than traditional solutions?
Cloud-based disaster recovery offers several advantages, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. It is often considered more reliable and efficient compared to traditional on-premises solutions.
Who should be part of the disaster recovery team?
The disaster recovery team should include individuals from IT, operations, management, and other critical departments. Each member should have a defined role and responsibilities during testing and actual disaster recovery efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-thought-out and thoroughly tested disaster recovery plan is vital for businesses to navigate through potential disasters without significant disruptions. By following the outlined components.
You may also like to know more about
- 6 Steps to a Successful Network Disaster Recovery Plan.
- What is Business Continuity Planning? Importance, Risk Assessment, & Core Objectives.
- Business Continuity Plan (BCP) Checklist.
- Disaster Recovery Planning To Ensure The Connectivity in Crisis.
- Wireless Emergency Kit: Staying Connected When it Matters.
- Safeguard Your Business with a Network Disaster Recovery Kit.
- 5G Mobile Broadband Kits to Supercharge Your Internet.
Stay connected with EXCEED ICT
Stay connected with EXCEED ICT by joining our social networks (given at footer). Get the latest updates, news, and tips for enterprise device deployment. Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn for the best enterprise device deployment solutions.
Help us to improve our enterprise by rating us on Google Maps. Your feedback and comments are valuable to us and will be used to make our services even better.


 Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis