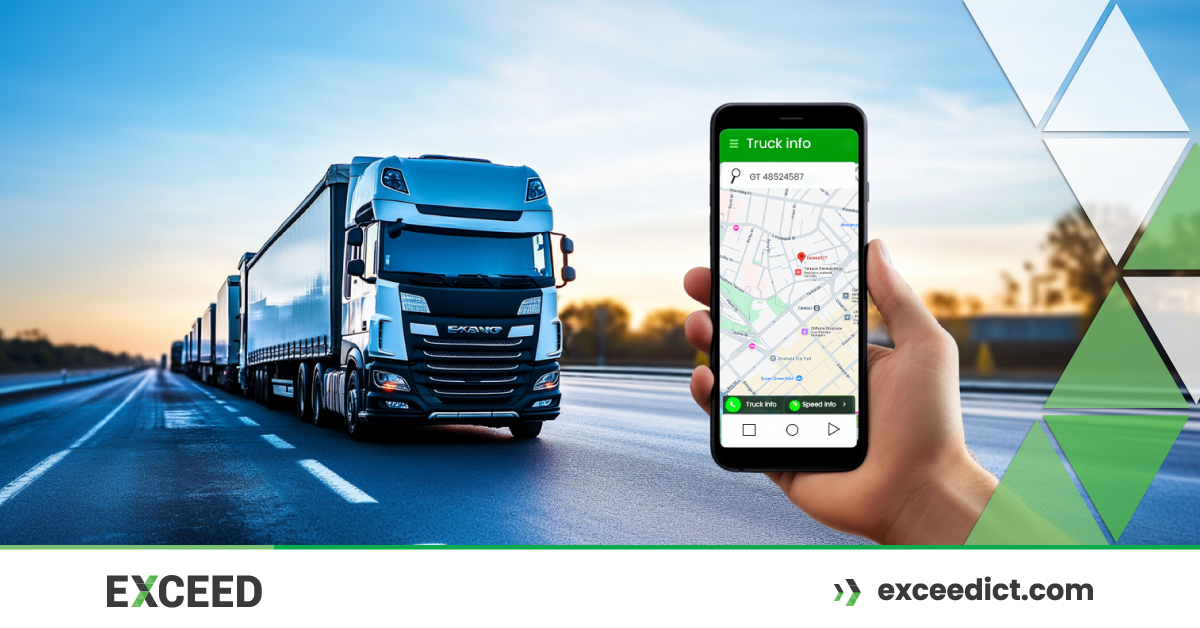
Vehicle telematics systems are advanced technological solutions designed to provide real-time data on the performance, location, and overall status of vehicles. They combine various elements such as GPS, communication systems, sensors, and on-board diagnostics to give vehicle owners, fleet managers, and businesses insightful information about the vehicles they manage.
These systems are used across industries for improving safety, reducing operational costs, and optimising fleet management, among other applications.
What is a Vehicle Telematics System?
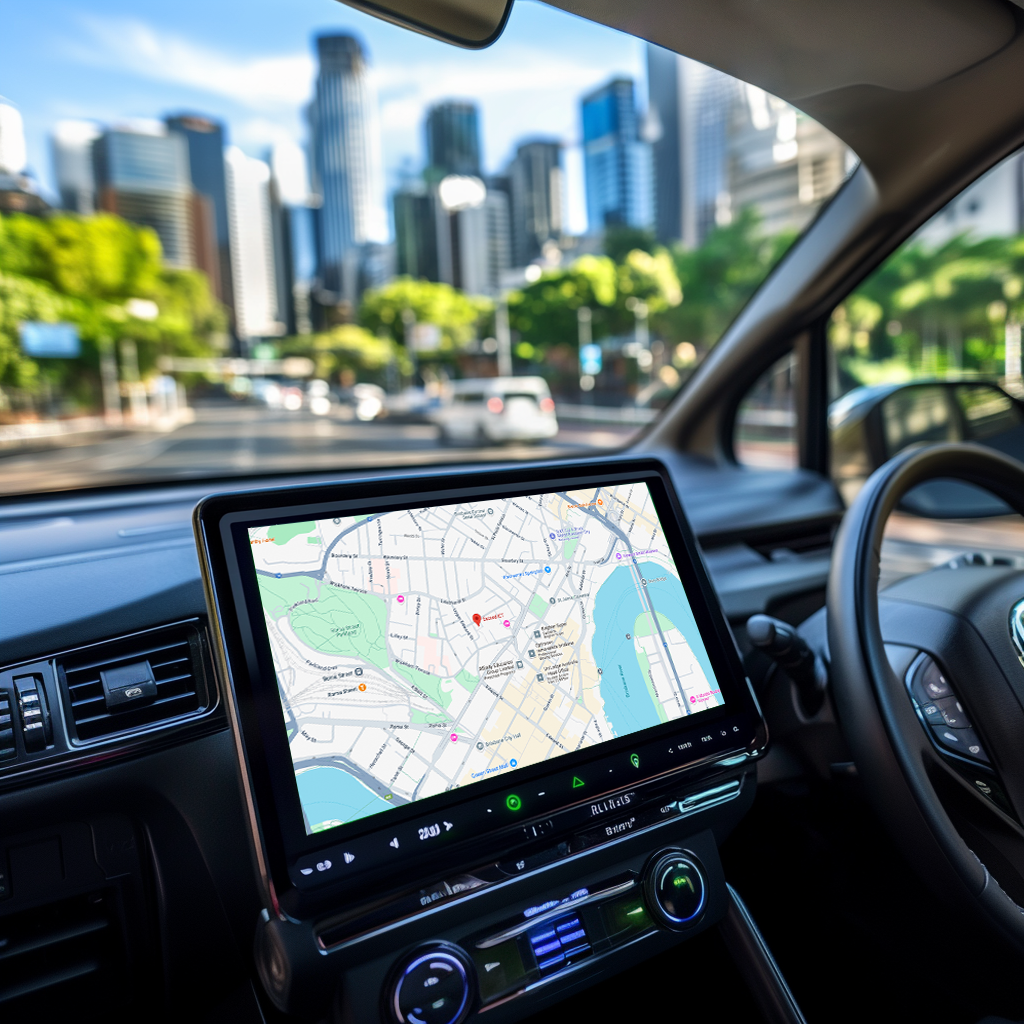

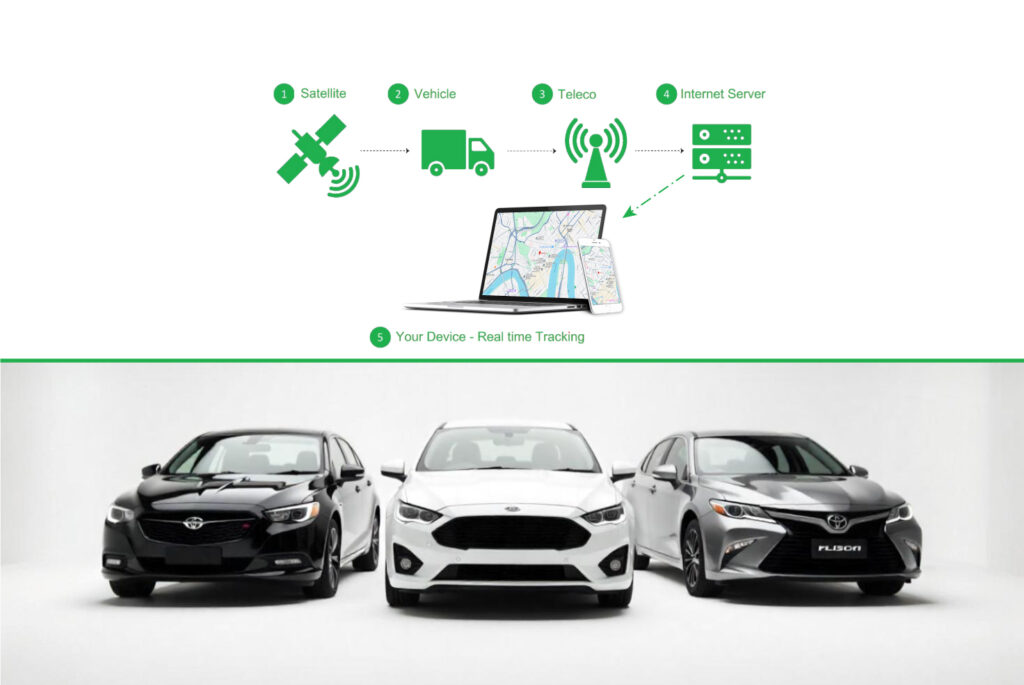
Vehicle telematics is the technology that integrates telecommunications and vehicle diagnostics to monitor and track vehicle performance, location, and condition. The system is typically built around an on-board telematics control unit (TCU), which collects data from the vehicle’s various systems and communicates this information to a central server or cloud platform. The data provided can range from GPS locations to vehicle health metrics like fuel consumption, tire pressure, and engine diagnostics.
While telematics was initially developed for commercial vehicle fleets, it has rapidly become common in personal vehicles and is increasingly integrated into autonomous driving technologies.
Key Components of a Vehicle Telematics System
Telematics Control Unit (TCU): The TCU is the heart of the system. It is an embedded device installed in the vehicle that collects data from other components, processes the information, and sends it to a remote server for analysis. The TCU can communicate wirelessly through cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or satellite signals.
GPS & Satellite Communication: GPS systems are critical in tracking the vehicle’s location and providing real-time navigation. This allows fleet managers and individuals to track the vehicle’s movements and analyse routes and driving behavior.
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II): The OBD-II system is integrated into most modern vehicles and monitors various aspects of the vehicle’s health, such as engine performance, emissions, and fuel efficiency. It feeds data directly to the telematics system, allowing vehicle owners and fleet managers to track any issues in real-time.
Sensors & Cameras: Modern telematics systems also incorporate additional sensors and cameras to provide more granular data, such as tire pressure, braking performance, speed, and driver behavior. This data can be crucial for safety features, route optimisation, and predictive maintenance.
Communication Interface: Wireless communication technologies such as cellular (3G, 4G, or 5G), Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi allow the telematics system to send data to cloud servers. The communication interface is vital for real-time updates and notifications regarding vehicle status.
How Does a Vehicle Telematics System Work?
A vehicle telematics system works by collecting data from various sources within the vehicle and transmitting this data to a central platform. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Data Collection: Sensors, GPS, and the vehicle’s diagnostic systems (such as OBD-II) collect real-time data on vehicle performance, location, fuel consumption, tire pressure, speed, and other critical parameters.
Data Transmission: The collected data is transmitted wirelessly via cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth to a cloud server. This step is vital for real-time tracking and remote monitoring.
Data Analysis: Once the data is transmitted to a central platform, it is analysed and processed. Advanced analytics can identify trends, provide alerts, and generate reports on vehicle performance, maintenance needs, driver behavior, etc.
Actionable Insights: Based on the analysed data, actionable insights can be provided to the vehicle owner or fleet manager. This can include route optimisation, maintenance alerts, fuel-saving tips, or driving behavior analysis.
Benefits of Using a Vehicle Telematics System
Improved Fleet Management: For businesses managing fleets of vehicles, telematics systems allow managers to track and monitor vehicles in real-time. This enables optimal route planning, reducing fuel costs, ensuring timely deliveries, and improving driver safety by monitoring behavior.
Increased Vehicle Safety: Telematics systems enhance safety by providing real-time insights into driver behavior (e.g., speed, braking patterns), which helps in reducing accidents. Many systems also offer emergency alert features, sending automatic distress signals in case of accidents.
Cost Savings: Telematics helps save money by offering insights on fuel consumption, maintenance schedules, and vehicle performance. With real-time monitoring, fleet managers can reduce fuel waste, improve route efficiency, and avoid costly repairs by identifying vehicle issues early.
Better Maintenance and Vehicle Health: Telematics allows owners and fleet managers to schedule regular maintenance based on real-time vehicle health data. It helps monitor engine performance, tire pressure, and other important metrics, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and prolonging vehicle life.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Telematics helps optimise routes and reduce idle time, contributing to fuel savings and lower carbon emissions. By ensuring that vehicles are running at peak efficiency, businesses and individuals can reduce their overall environmental footprint.
Enhanced User Experience: Telematics systems can provide drivers with useful information such as vehicle diagnostics, traffic updates, and navigation assistance. This can improve the driving experience and make managing the vehicle easier and more convenient.
Applications of Vehicle Telematics Systems
Fleet Management: Fleet management is one of the primary applications of telematics systems. Businesses use these systems to track their vehicles, optimise routes, monitor driver behavior, and ensure timely maintenance, all of which contribute to more efficient operations.
Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): Insurance companies are increasingly using telematics to offer usage-based insurance. With UBI, the insurance premium is based on how the driver behaves behind the wheel. By monitoring driving patterns through telematics, insurers can reward safe drivers with lower premiums.
Personal Vehicles: For individual drivers, telematics systems offer real-time diagnostics and maintenance alerts. They also help drivers track fuel consumption, optimise routes, and even monitor driver safety to encourage safer driving habits.
Smart Cities: Telematics plays a key role in the development of smart cities by providing data that can be used for traffic management, infrastructure planning, and reducing congestion. The data gathered can also be utilised to improve public transportation systems.
Challenges and Limitations of Vehicle Telematics
Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Telematics systems collect vast amounts of data, which raises concerns about data privacy and security. Vehicle owners must trust that their data is being securely stored and not misused.
Initial Cost: For individual vehicle owners and small businesses, the initial cost of installing a telematics system can be a barrier. However, the long-term savings and benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Signal Issues: In some areas with poor network coverage, telematics systems may face difficulties in transmitting data. This can lead to gaps in tracking or delays in receiving important updates.
Technical Issues and Maintenance: Telematics systems rely on sensors, hardware, and software, all of which need regular maintenance. If any component fails, it can result in incorrect or incomplete data collection.
The Future of Vehicle Telematics Systems
The future of vehicle telematics is focused on integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and 5G connectivity. These technologies will enhance data analysis, enabling even more sophisticated insights into vehicle performance, predictive maintenance, and driver safety. Additionally, telematics will play a critical role in the future of autonomous vehicles and electric vehicles, offering essential data for safe operation and energy management.
Conclusion: Vehicle telematics systems are rapidly transforming the automotive industry by offering a wealth of data and insights that can improve vehicle safety, fleet management, and operational efficiency. Whether used for managing business fleets or for personal vehicle maintenance, the adoption of telematics systems is poised to drive significant changes in the way we drive, maintain, and operate vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vehicle telematics systems
What does telematics do in a car?
Telematics in a car provides real-time data about the vehicle’s location, speed, fuel efficiency, and driving habits. It uses GPS and sensors to track performance and improve fleet management.
Can you turn off vehicle telematics?
Yes, telematics systems can be turned off in most vehicles, but it depends on the manufacturer and the system in use. Some may require technical support.
What is telematics in a car in Australia?
In Australia, telematics in cars refers to the use of GPS and communications technology to monitor and manage vehicle performance, often used in fleet management.
Is telematics the same as GPS?
No, while GPS is a component of telematics, telematics is a broader system that includes GPS, vehicle sensors, and data analytics to provide detailed vehicle information.
Is telematics a tracker?
Yes, telematics can function as a tracker by using GPS to monitor the vehicle’s location, speed, and routes in real time.
Why do I need telematics?
Telematics helps improve vehicle performance, enhances safety, reduces costs, and provides valuable insights for businesses to manage fleets more efficiently
Is telematics used for driver monitoring?
Yes, telematics systems can monitor driver behavior, including speed, braking patterns, and idle time, providing feedback to improve safety and reduce accidents.
Can telematics help with insurance?
Telematics can be used by insurance companies to offer pay-as-you-drive or usage-based insurance policies, rewarding safe driving habits with lower premiums.
Is telematics secure?
Telematics systems generally use encryption to protect data. However, like any technology, ensuring the system is regularly updated and maintained is essential for security.
We Also Provide
Telecoms Expense Management, Device Deployment, Mobile Fleet management, Telstra enterprise Mobility, Telstra mobility Managed Services.
Improve Business Core values, Business Consulting, Network Management, Telstra Expense Management and many more Services.